The cause of fading (discoloration) of printed matter
Time:2024-07-15
Views:2087
1, ink drying process of discoloration and fading
In the printing process, the ink color of the newly printed ink is compared with the ink color after drying, the ink color of the newly printed ink is darker, and after a period of time, the ink color will become lighter after the impression is dried; This is not the ink is not light fading, discoloration problem, mainly the ink in the drying process penetration and oxidation of the conjunctiva caused by discoloration. The relief ink is mainly permeated and dried, and the ink layer is relatively thick for the products just printed from the printing machine, and it will take some time for the permeation and oxidation conjunctiva to dry.
2, the ink itself is not light and discoloration and fading
Ink after the light fading, discoloration is inevitable, all ink after the light will have different degrees of fading, discoloration phenomenon. Light color inks fade and change color seriously after long exposure to light. Yellow, crystal red, green fade quickly, blue, blue, black fade slowly. In the actual work, when adjusting ink, we should try to choose good light performance ink, adjust light color should pay attention to the light resistance of the ink after diluting, and consider the consistency of light resistance between several colors of ink when deploying ink.
3, the acid and alkali of paper on the ink fading, color change
Under normal circumstances, paper is weakly alkaline. The ideal paper PH value is 7, is neutral, because in the papermaking process, need to add caustic soda (NaOH), sulfide, chlorine and other chemicals, in the pulping and papermaking process is not properly treated, may make the paper acidic or alkaline.
The alkalinity of paper comes from the papermaking process itself, and some are caused by adhesives containing alkaline substances used in post-binding production. If you use paucine and other alkaline adhesive, then the alkaline substance will penetrate into the paper fiber, and the ink color particles on the surface of the paper will react chemically, causing it to fade and change color. When selecting raw materials and adhesives, it is necessary to analyze the physical and chemical properties of adhesives, paper, and the effects of acid and alkali on ink, paper, electrochemical aluminum foil, gold powder, silver powder and laminating film.
Inks made of inorganic pigments are generally poor in acid and alkaline resistance, and organic pigments are better in acid and alkaline resistance, especially medium blue and deep blue inks will fade when they encounter alkali. Yellow alkali color becomes red, hot printing of electrochemical aluminum foil, printing gold encounter alkaline substances will become ancient yellow, no luster, often the paper is weak alkaline more, in the later printing binding production encountered alkaline adhesive, if packaging decoration printing products are packaging alkaline substances such as soap, soap, washing powder, etc., should consider the ink alkali resistance, saponification resistance performance.

4, the other properties of the paper on the impact of ink fading, color change
① Surface smoothness of paper
The smoothness of the paper surface is closely related to the copying of imprinting, and the uneven paper often requires greater pressure to make the ink have good contact with it. Such as ink viscosity, fluidity, ink layer thickness to maintain a certain amount, increase the pressure often increase the print spread area, at the same time, the paper of the concave part, but still poor contact, for example: coated paper and newsprint printed in the same plate printing effect has a large difference, can obviously compare the different replication effects.
② Absorbency of paper
The size of the absorbability of the paper is also directly related to the replication effect, usually in the printing of loose paper, if the ink fluidity is large, the viscosity is small, the paper will absorb more ink layer connection material, if the diameter of the pores is greater than the diameter of the pigment particles, then even the pigment will be inhaled, which reduces the saturation of the impression. The thickness of the ink layer needs to be appropriately increased.
However, increasing the thickness of the ink layer will cause "spreading" at the moment of imprinting, affecting the effect of imprinting replication. The paper with small absorption can make most of the ink film appear on the surface of the paper, so that the imprinted ink layer has a better saturation.
③ Permeability of paper
Paper permeability is large, will make the ink layer thickness thin, paper surface pores are large, but also make part of the pigment particles are infiltrated into the paper at the same time, so the color has the feeling of thinning. To this end, the use of rough surface, loose texture of paper should pay attention to discoloration.
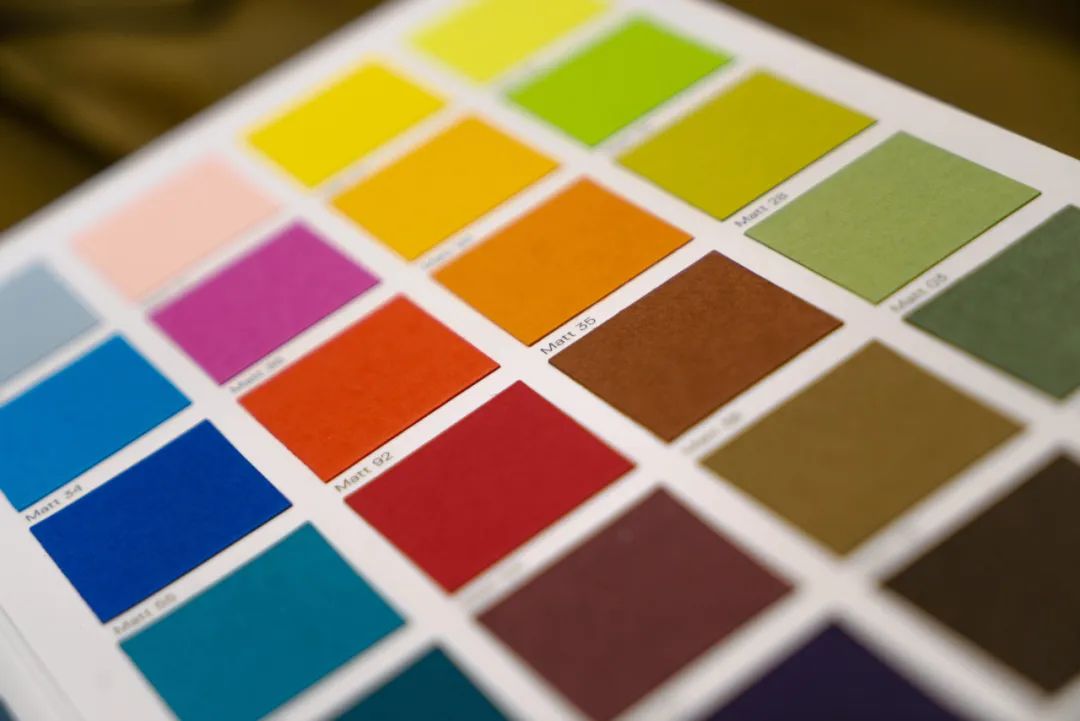

5, temperature caused by fading, discoloration
Some packaging and decoration trademarks are attached to rice cookers, pressure cookers, electronic stoves and other kitchen utensils, and the ink quickly fades and changes color under high temperature. The heat resistance of the ink is about 120℃. The offset press and other printing machinery and equipment operate at high speed when working, the ink and the ink roller, the ink and the plate plate are heated at high speed, and the ink will also generate heat at this time, which will make the heat resistant pigment discoloration.
6, printing color sequence caused by improper fading and discoloration
The commonly used color sequence of the four-color plate monochrome machine is: Y, M, C, BK, the four-color machine is the reverse color sequence: BK, C, M, Y, what is printed after the four colors of ink, which will affect the fading and discoloration of the printing ink.
When arranging the printing color sequence, the light color and the ink that is easy to fade and discolor are printed first, and the deep color ink is printed after the printing, which can prevent fading and discoloration.
7, the amount of dry oil caused by improper fading, discoloration
The amount of red dry oil and white dry oil added to the ink does not exceed 5% of the ink amount, and the amount is about 3%. The dry oil has a strong catalytic effect in the ink layer, and it is heated. If the amount of dry oil is excessive, it will make the ink fade and discolor.
8, the effect of emulsification
Offset printing plate to wet the blank part of the plate with wetting liquid, offset printing is the first water on the ink, water will inevitably appear emulsification phenomenon.
The color of the ink will be diluted after emulsification, but it can restore the original color after the evaporation of water, so the greater the water, the greater the emulsification, it will cause discoloration. In particular, the color inks with completely different degrees of emulsification are adjusted together, and the phenomenon of discoloration is particularly prominent.
9, storage environment impact
Most printed products are stored for a long time, and it is inevitable that they will be yellow, which is because the fiber in the paper contains more lignin and discoloration. In addition, offset four-color dot overprinting color printing products, under the sunlight, for a long time, wind and rain, because the pigment is not light, heat resistant discoloration or fading.